Research Highlights : The mechanism of instabilities of deposit patterns left after the evaporation of a particle-laden liquid droplet was elucidated using a Monte Carlo method
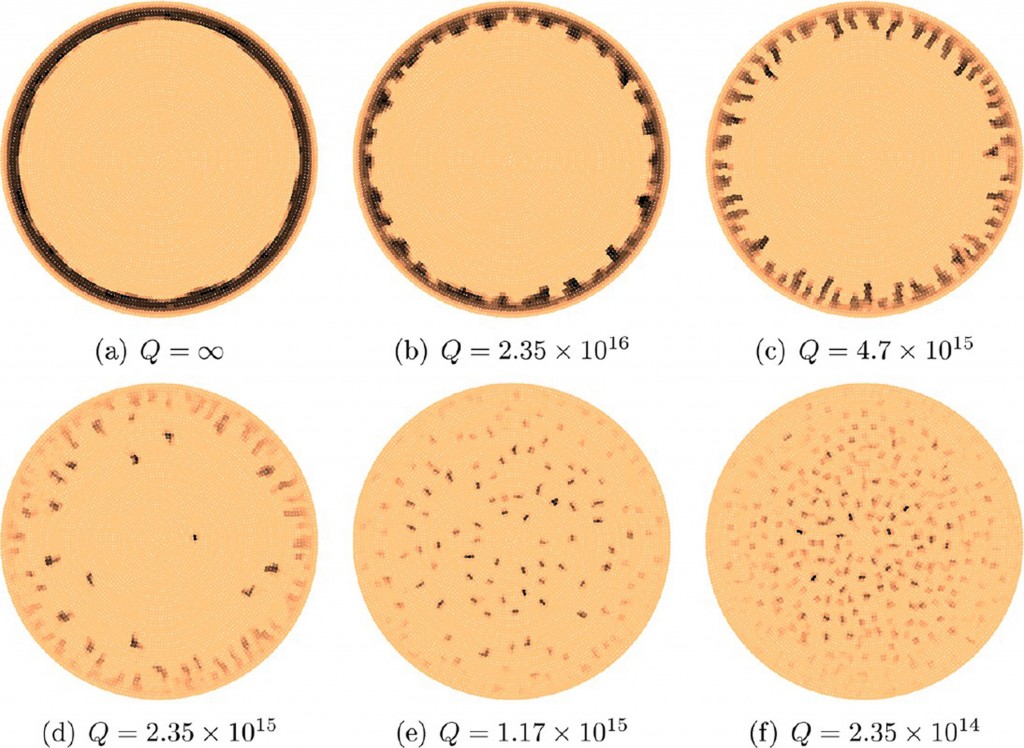
Abstract : The characteristics of several patterns left after the evaporation of a particle-laden liquid droplet are investigated by using a coarse-grained lattice model. The model includes both evaporative convection and the Brownian motion of weakly interacting particles. The model is implemented by using a Monte Carlo method to investigate the different deposit patterns near the contact line. It was found that different deposit patterns form depending on the interplay between the convective transport and the deposition of interacting particles. The patterns were analyzed by varying the ratio of the convective forces to the interaction forces as well as the size and the number of particles. It was also found that the ring-like patterns are formed when the convective potential dominates the interactions of particles, whereas either wave-like or island-like patterns form in the opposite case. Finally, the average thickness of the wave-like patterns is mainly determined by evaporation rates
Resource : leopard, lion, falcon, cheetah
Representative Thesis : N. Jung, C. S. Yoo*, and H. Leo* (2014) Instability Deposit Patterns in an Evaporating Droplet. Journal of Physical Chemistry B 114, 2535-2543. * co-corresponding authors