Research Highlights : Determining dimer structure of HBD and its antimicrobial activity
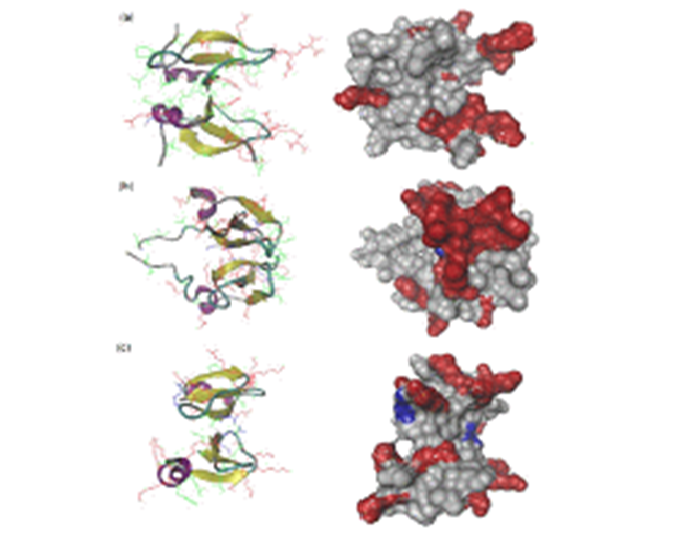
Abstract : The stable dimeric structures of human b-defensin (HBD)-3 and -28 have been first computationally identified via a protein docking approach in conjunction with all-atom molecular dynamic simulation. We found that both HBD dimers contain an extended b-sheet platform stabilised mainly by the interaction of second b-sheets and further investigated interaction
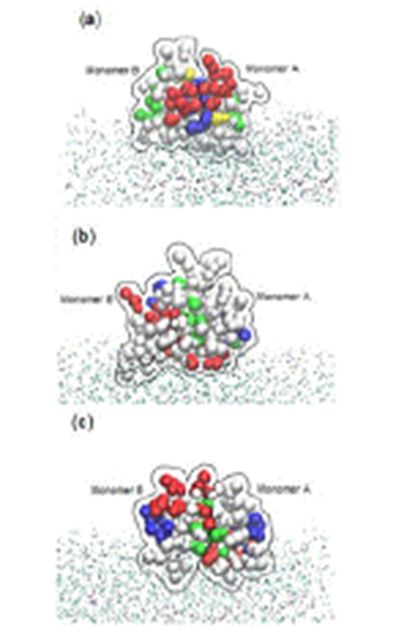
mechanisms of these dimers including HBD-2 against 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-phosphatidylglycerol membrane bilayer by using coarse-grained model combined with the ElNeDyn network. The extended b-sheet platform of the HBD dimer stayed over the bilayer due to the attachment of the amphipathic region located on one side of the b-sheet platform. The hydrophobic residues of HBDs on the surface interact with the hydrophobic tails of the lipids, whereas the positively charged residues interact with the lipid polar head groups. Finally, antimicrobial nature of HBD-2, HBD-3 and HBD-28 dimers is found to be kept because they are not detached in interacting with the membrane
Resource : NTU-HPC, UNIST-HPC
Representative Thesis : Wen Wen Chen, Yong-Jin Yoon, Su Jan Susanna Leong*, and Sang Kyu Kwak*, “Study of Dimerization of HBD and Its Interactions with POPG Membrane”, Molecular Simulation, 39(11), 849-859, 2013